Radon is a colorless, odorless, and radioactive gas that originates from the natural decay of uranium in soil, rock, and water. This gas can seep into homes through cracks and openings in the foundation, floors, and walls. Exposure to high levels of radon can lead to serious health issues, including lung cancer.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), radon is responsible for up to 14% of lung cancers globally. The gas accumulates in enclosed spaces, posing a significant risk to indoor air quality. Ensuring your home is safe from radon is crucial, making the selection of an effective radon mitigation system imperative.
Table of Contents
Testing for Radon
The Importance of Radon Testing
Before investing in a radon mitigation system, it’s essential to test your home for radon levels. Radon Testing can determine whether your home has high radon levels that require mitigation. Radon levels are measured in picocuries per liter (pCi/L), and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends action if levels exceed 4 pCi/L.
Regular testing can help homeowners detect radon levels early, preventing prolonged exposure. It is particularly important in areas known to have high radon concentrations, but every home should be tested regardless of geographical location.
Types of Radon Tests
- Short-term tests: These tests typically last between 2 to 90 days. They are a quick way to get an initial reading of radon levels in your home. Short-term tests can be conducted using various devices, such as charcoal canisters, alpha track detectors, and continuous radon monitors. These tests are useful for a preliminary assessment, especially if you need immediate results.
- Long-term tests: These tests last longer than 90 days and provide a more accurate average of radon levels over time. They are particularly useful in homes where radon levels fluctuate. Long-term tests often use alpha track detectors or electret ion chambers, which remain in place for several months. The extended testing period offers a more comprehensive picture of radon exposure, making it ideal for confirming the need for mitigation.
Choosing the Right Radon Mitigation System
Active Soil Depressurization (ASD)
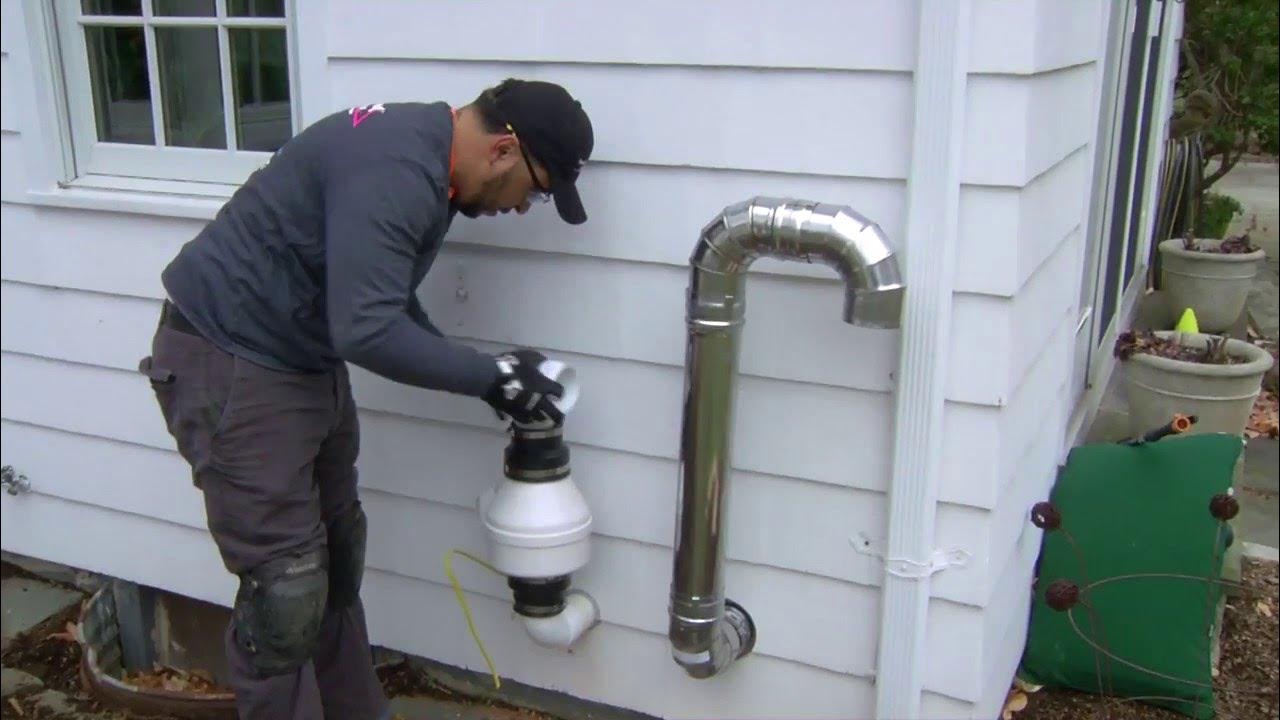
Active Soil Depressurization is the most common and effective radon mitigation method. This system uses a vent pipe and fan to draw radon from beneath the house and expel it outside.
The fan creates a vacuum that prevents radon from entering the living spaces. ASD systems can be installed in various ways, depending on the home’s foundation type.
Sub-Slab Depressurization
This method involves inserting a pipe through the foundation slab into the soil beneath. A fan is used to draw the radon gas from under the slab and vent it outside. Sub-slab depressurization is effective for homes with concrete slab foundations.
The system reduces radon levels by preventing the gas from entering the home through the foundation. Installation typically requires drilling a small hole in the slab and sealing the pipe around it to ensure an airtight connection.
Drain-Tile Suction
For homes with a drain-tile system, a fan and pipe are connected to the existing drain tiles to draw radon from beneath the house and release it outside. This method is ideal for homes with perimeter drain systems.
The fan creates a negative pressure zone, capturing radon before it can enter the home. Installation involves connecting the mitigation system to the drain tiles and ensuring proper venting to the outside.
Other Radon Mitigation Methods
Sealing
Sealing cracks and openings in the foundation is an essential part of radon mitigation. However, it is generally used in conjunction with other methods rather than as a standalone solution. Sealing reduces the flow of radon into the home but does not eliminate it entirely.
It is an important step in any mitigation strategy, as it enhances the effectiveness of other mitigation techniques by minimizing entry points for radon.
House or Room Pressurization
This method involves using a fan to create positive pressure in the home or specific rooms, preventing radon from entering. It can be effective but is typically less reliable than other methods. Pressurization works best in homes with relatively low radon levels and minimal air leakage.
The technique requires careful balancing of indoor and outdoor air pressure to ensure that radon does not seep in through unsealed areas.
Hiring a Professional vs. DIY
Professional Installation
Hiring a professional radon mitigation contractor ensures that the system is installed correctly and effectively. Professionals have the necessary training, experience, and equipment to properly assess radon levels and install the most suitable system.
North Central Radon is familiar with local building codes and can ensure that the installation complies with all regulations. Professional Radon System installation often includes a warranty, providing peace of mind that the system will function as intended. North Central Radon Contractors also conduct post-installation testing to verify that radon levels have been successfully reduced.
DIY Options
For those who prefer a hands-on approach, there are DIY radon mitigation kits available. However, DIY methods may not be as effective or reliable as professional installations. It’s crucial to follow all instructions carefully and consider professional assistance if needed.
DIY kits typically include basic components like vent pipes and fans, but they may lack the advanced features and materials used by professionals. Homeowners attempting a DIY installation should be prepared to conduct multiple tests to ensure the system’s effectiveness and make adjustments as necessary.
Costs and Maintenance of Radon Mitigation Systems
Initial Costs
The cost of a radon mitigation system can vary depending on the home’s size, foundation type, and the chosen mitigation method. On average, homeowners can expect to spend between $800 and $2,500 for a professionally installed system.
This investment includes materials, labor, and post-installation testing. While the initial cost may seem high, the long-term health benefits and potential increase in home value make it a worthwhile expense. DIY kits are generally less expensive, ranging from $500 to $1,000, but they may require additional time and effort to install correctly.
Ongoing Maintenance
Radon mitigation systems require regular maintenance to ensure continued effectiveness. This includes checking the fan and vent pipes, sealing any new cracks in the foundation, and conducting periodic radon tests to monitor levels.
Fans may need replacement every 5 to 10 years, and electrical components should be inspected regularly. Homeowners should also ensure that the vent pipes remain clear of obstructions, such as leaves or debris. Regular testing, at least once a year, is crucial to verify that the system is maintaining low radon levels.
Benefits of Radon Mitigation
Health Benefits
The primary benefit of installing a radon mitigation system is the significant reduction in lung cancer risk. By lowering radon levels in your home, you protect your family’s health and well-being.
Reducing radon exposure can lead to a lower incidence of respiratory issues and other health problems associated with poor indoor air quality. The long-term health benefits far outweigh the initial investment in a mitigation system.
Increased Home Value
Homes with radon mitigation systems can have increased market value, as potential buyers are often concerned about radon exposure. A documented mitigation system can be a selling point, providing peace of mind to prospective buyers.
Buyers are more likely to consider a home that has been tested and mitigated for radon, as it eliminates a potential health risk. Additionally, a mitigation system can enhance the overall appeal of the property, making it more attractive in a competitive real estate market.
Conclusion
Investing in a radon mitigation system is a crucial step in ensuring the safety and health of your home environment. By understanding the risks of radon, testing your home, and choosing the right mitigation method, you can effectively reduce radon levels and protect your family from its harmful effects.
Regular maintenance and testing will ensure that the system continues to function effectively, providing long-term protection. The health benefits, combined with the potential increase in home value, make radon mitigation a wise and necessary investment for any homeowner.