Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that is present in the soil and rocks. It is odorless, colorless, and tasteless, making it difficult to detect without proper testing. When radon is present in the air, it can be inhaled into the lungs, where it breaks down into tiny radioactive particles. These particles can damage the DNA in lung cells, increasing the risk of lung cancer over time. While radon exposure is a risk for everyone, children are particularly vulnerable to its effects.
In this article, we will explore the dangers of radon exposure for children and what parents and caregivers can do to protect them.
Table of Contents
The Dangers of Radon Exposure for Children
Radon exposure can have serious health consequences for children, including an increased risk of lung cancer and other respiratory problems. Children are particularly vulnerable to these effects because their lungs are still developing and they breathe more rapidly than adults.
Exposure to radon is the leading cause of lung cancer among non-smokers, and it is responsible for about 21,000 deaths in the United States each year. Children who are exposed to high levels of radon are at increased risk of developing lung cancer later in life. In fact, the Environmental Protection Agency estimates that about 5,000 cases of lung cancer in children each year are due to exposure to radon.
In addition to lung cancer, radon exposure has also been linked to other health problems in children, including respiratory infections, asthma, and even leukemia.
It is important to note that these health effects may not become apparent until years or even decades after the exposure has occurred.
The Science Behind Radon Exposure and Children
The science behind radon exposure and its effects on children is complex. Radon is a radioactive gas that is produced by the decay of uranium in the soil and rocks. When radon is present in the air, it can be inhaled into the lungs, where it breaks down into tiny radioactive particles.
These particles can damage the DNA in lung cells, increasing the risk of lung cancer over time. Children are particularly vulnerable to these effects because their lungs are still developing and they breathe more rapidly than adults.
Research has shown that children are more radiosensitive than adults, meaning that they are more susceptible to the effects of radiation exposure. This is because children’s cells are dividing and growing rapidly, which makes them more vulnerable to damage from radiation.
Additionally, children’s lungs are smaller and less developed than those of adults, which means that they may be more susceptible to damage from radon particles.
How to Protect Children from Radon Exposure
The most important thing that parents and caregivers can do to protect children from radon exposure is to test the home for radon. Radon testing is the only way to know for sure if your home has high levels of radon.
Testing is easy, inexpensive, and can be done by a certified radon testing professional or with a do-it-yourself test kit. If radon levels are found to be high, there are steps you can take to reduce exposure, including sealing cracks and gaps in the foundation and installing a radon mitigation system.
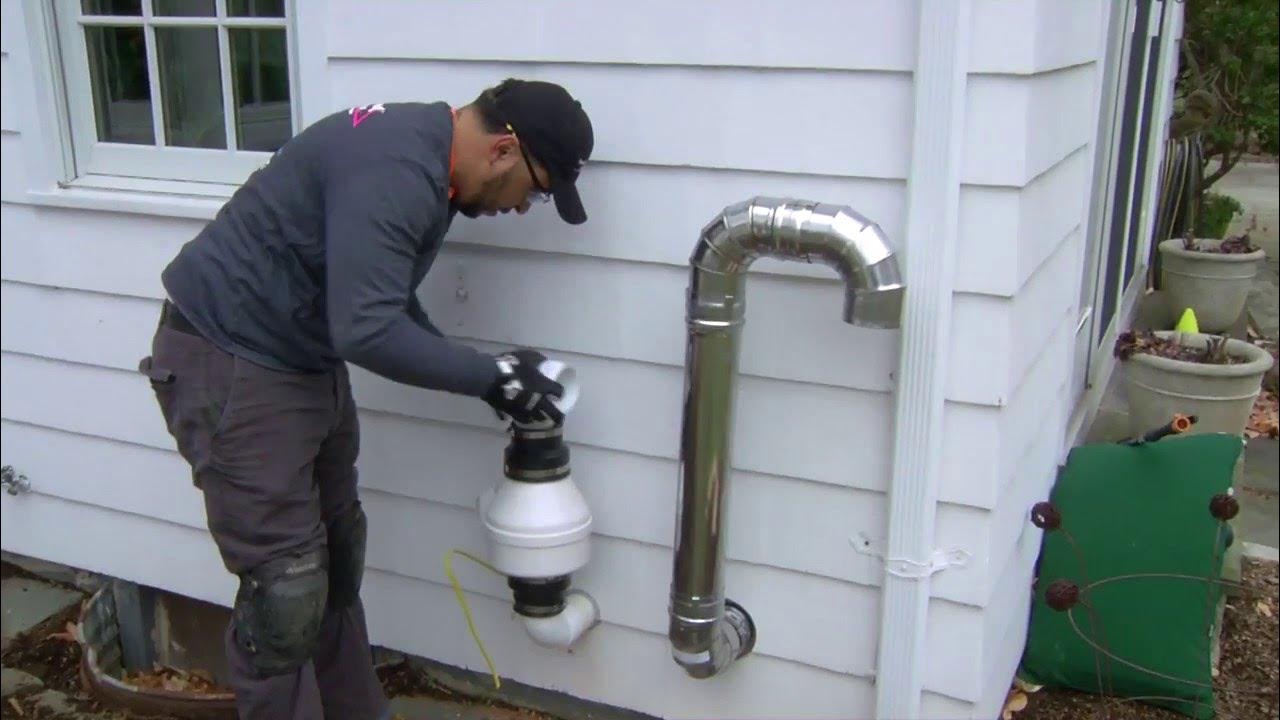
Sealing cracks and gaps in the foundation is an important step in reducing radon exposure. Radon can enter the home through cracks and gaps in the foundation, so sealing these areas can help to reduce the amount of radon that enters the home. Radon mitigation systems are also an effective way to reduce radon exposure. These systems work by venting radon gas from the soil beneath the home to the outside air.
It is also important to take steps to reduce radon exposure in schools and childcare facilities. Radon testing should be done in all schools and childcare facilities, and mitigation measures should be taken if high levels of radon are found. Parents and caregivers can also advocate for radon testing and mitigation in schools and childcare facilities.
Conclusion
Radon exposure can have serious health consequences for children, including an increased risk of lung cancer and other respiratory problems. It is important for parents and caregivers to take steps to protect children from this invisible threat, including testing the home for radon and implementing appropriate mitigation measures. By taking these steps, you can help to ensure that your children are protected from the dangers of radon exposure.
If you are concerned about radon exposure in your home or childcare facility, contact a certified radon testing professional to conduct a test. If high levels of radon are found, take action to reduce exposure by sealing cracks and gaps in the foundation and installing a radon mitigation system. By taking these steps, you can help to ensure that your children are protected from the dangers of radon exposure.
Remember, radon testing is the only way to know for sure if your home or childcare facility has high levels of radon. Don’t wait, test your home today and take action to protect your children from the dangers of radon exposure.